
Problemy Gematologii i Perelivaniia Krovi 16(7): 46-48, 1971 Hemolytic disease of the newborn in maternal and fetal blood factor M incompatibility. Hemolytic disease in the newborn caused by ABO incompatibility 12 cases treated with exchange transfusion. Secondary anemia of the hemolytic illness of the newborn linked to ABO feto-maternal incompatibility French Society of Hematology, 21 February, 1966. Gynecologie et Obstetrique 65(2): 141-160, 1966Ĭlinico-statistical considerations on newborn infants treated with exchange transfusions for hemolytic disease caused by Rh isoimmunization or ABO incompatibility and for hyperbilirubinemia of non-immunological causes in full-term newborn infant. Hemolytic disease caused by Rhesus incompatibility in the 1st newborn. International Record of Medicine 174: 349-351, 1961 The rare factor, Rh variant: a case report of hemolytic disease of the newborn infant due to D-u factor incompatibility. Serologically typical cases of hemolytic disease of newborn with ABO incompatibility. Revista del Colegio Medico de Guatemala 13: 188-196, 1962 Report on 15 cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn due to Rh incompatibility.

JournaldeMedecinedeBordeauxetduSud-Ouest125(10):469, 1948 Two cases of hemolytic disease of the newborn due to incompatibility Rheus. Nouvelle Revue Francaise d'Hematologie 6(4): 537-543, 1966īreast feeding and hemolytic disease in newborn case of Rh incompatibility anemia with special reference to its course. Secondary anemia of the hemolytic disease of the newborn related to feto-maternal ABO incompatibility.

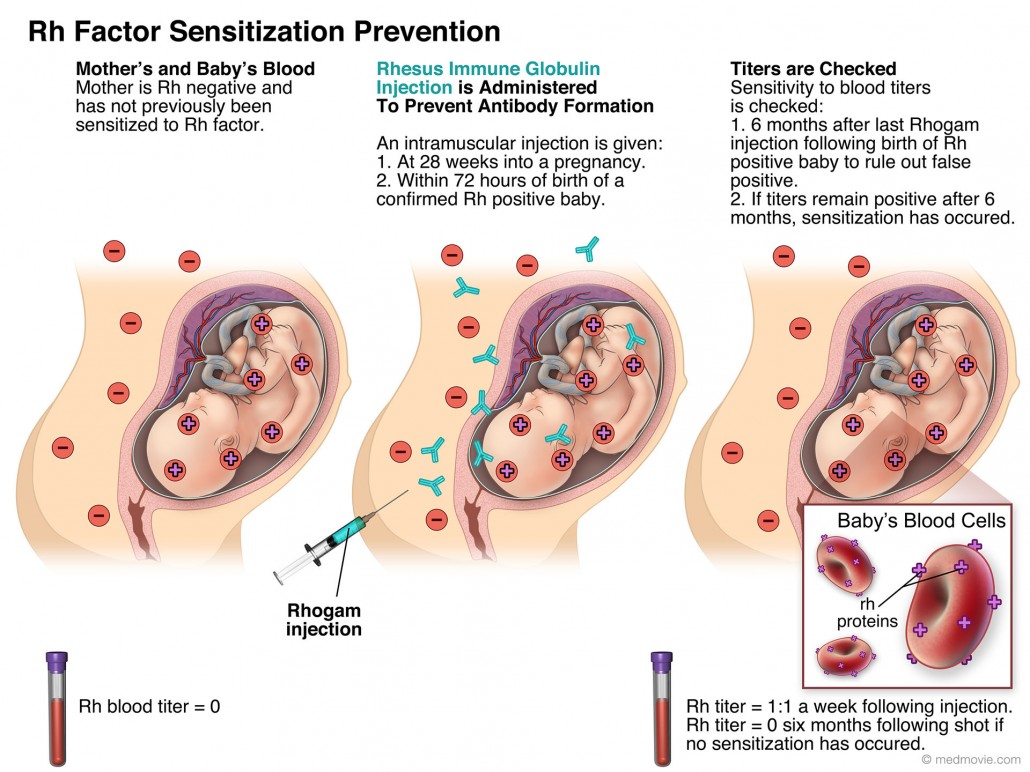
Rivista d'Ostetricia E Ginecologia Pratica 42: 411-418, 1960 During pregnancy, this organ contains and nourishes the fetus.On the use of prednisolone in hemolytic anemia of the newborn caused by fetomaternal Rh-factor incompatibility. Uterus: A muscular organ in the female pelvis. Umbilical Cord: A cord-like structure containing blood vessels. During pregnancy, ultrasound can be used to check the fetus. Ultrasound Exams: Tests in which sound waves are used to examine inner parts of the body. Rh Immunoglobulin (RhIg): A substance given to prevent an Rh-negative person's antibody response to Rh-positive blood cells.

Rh Factor: A protein that can be found on the surface of red blood cells. Prenatal Care: A program of care for a pregnant woman before the birth of her baby. Placenta: An organ that provides nutrients to and takes waste away from the fetus. Oxygen: An element that we breathe in to sustain life. Obstetrician–Gynecologist (Ob-Gyn): A doctor with special training and education in women's health. Miscarriage: Loss of a pregnancy that is in the uterus.
#Rh ifactor in compability skin
Jaundice: A buildup of bilirubin (a brownish yellow substance formed from the breakdown of red cells in the blood) that causes the skin to have a yellowish appearance. Induced Abortion: An intervention to end a pregnancy so that it does not result in a live birth. They are the basic units of heredity and can be passed from parent to child. Genes: Segments of DNA that contain instructions for the development of a person's physical traits and control of the processes in the body. Cells are the building blocks for all parts of the body.Ĭhorionic Villus Sampling (CVS): A procedure in which a small sample of cells is taken from the placenta and tested.Įctopic Pregnancy: A pregnancy in a place other than the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes.įetus: The stage of human development beyond 8 completed weeks after fertilization. Most cases are caused by iron deficiency (lack of iron).Īntibodies: Proteins in the blood that the body makes in reaction to foreign substances, such as bacteria and viruses.īreech Presentation: A position in which the feet or buttocks of the fetus would appear first during birth.Ĭells: The smallest units of a structure in the body. The procedure uses a needle to withdraw fluid and cells from the sac that holds the fetus.Īnemia: Abnormally low levels of red blood cells in the bloodstream. Amniocentesis: A procedure in which amniotic fluid and cells are taken from the uterus for testing.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
